SSDs are great (except they can also be the worst of drives), but they usually have less capacity than modern conventional drives. In 2013, 128GB is still a common size, and even a 256GB drive can only hold so much. At the same time, main memory is increasing and 8GB of RAM is quite common.
The increasing main memory will often reserve unnecessary space on your drive for hibernation and paging. This guide shows how to reclaim that space on Windows 7 and Windows 8 (but should work for any windows with minimal changes).
Hibernation is the process of writing all of the memory contents to disk before shutdown, making it possible to resume later without using any power from the battery in between. While this sounds useful, I find that I almost never use it. For shorter (less than a day) pauses I will use sleep instead of hibernate anyway, and for longer breaks it just makes sense to reboot. This is Windows, after all. In addition, writing 8GB to disk often will waste precious write-cycles on the SSD.
Paging means using disk space to augment the main memory when the latter is full. With today’s large main memories this will mostly happen when processing very large images, e.g. in Photoshop. Even with multiple virtual machines and several heavy apps running at the same time, my computer never resorts to paging. In any case, if your computer routinely resorts to paging, your problem is better solved by adding more memory.
Hibernation reserves as much space as your RAM, and the paging file usually reserves the same. With these two gone, you can use that space for something else.
Removing Hibernation
First make a shortcut on your desktop for a command prompt. Right click the desktop, select new shortcut, and type cmd.exe for the location.
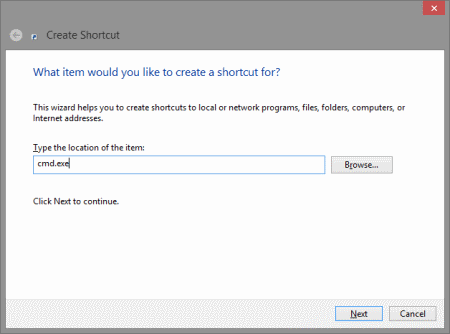
Create Shortcut for CMD.exe
Then, right-click the new shortcut, select run as administrator and type:
powercfg.exe /hibernate off
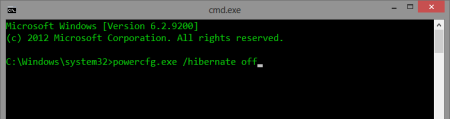
Hibernate Off
After hitting enter, the system will no longer hibernate. The hibernation file hiberfil.sys should also be gone. If you did not get any more disk space, check that there is no c:\hiberfil.sys (note that this is hidden system file, remember to enable the listing of such files in Windows Explorer), and delete any separate hibernation partition to reclaim the space. Disabling Paging This is easier, go to Control Panel, System and select the Advanced tab.
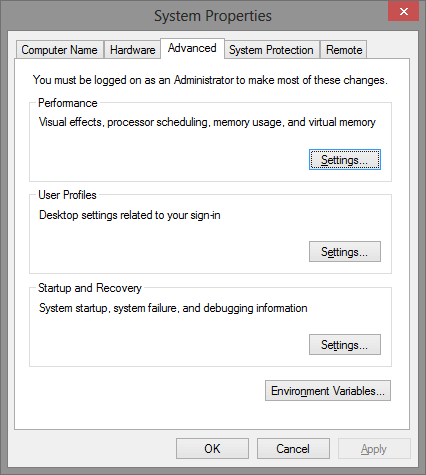
System Properties
From here, click Performance Settings and Change. When you are done there should be zero and None all over the place.
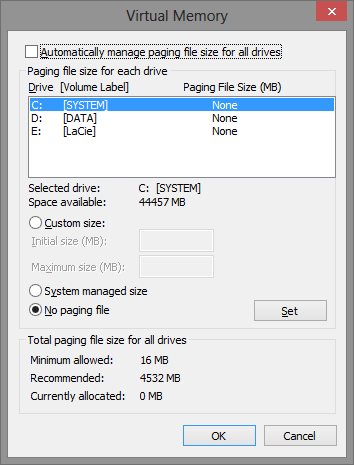
Virtual Memory Settings